Sampling & Resampling
Sampling
Three methods in applied machine learning
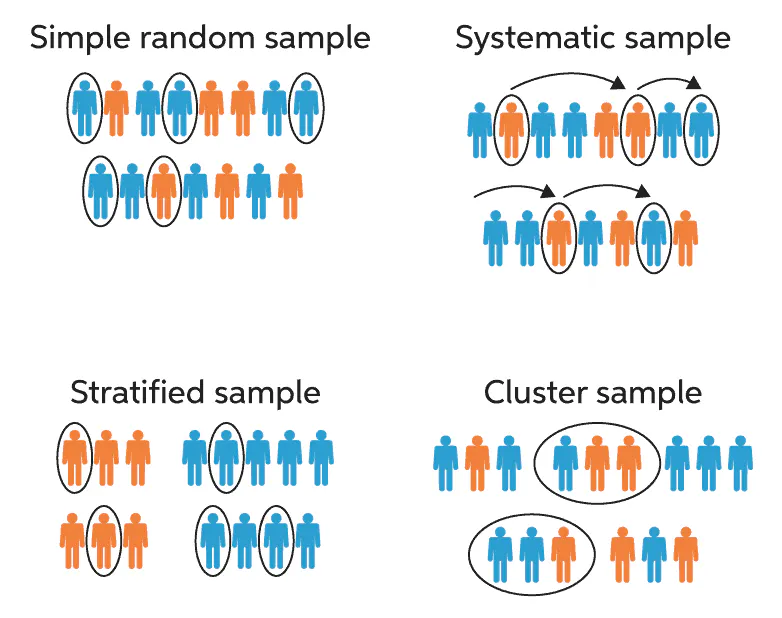
Simple Random Sampling
- Samples are drawn with a uniform probability from the domain.
Systematic Sampling
- Samples are drawn using a pre-specified pattern, such as at intervals.
Stratified Sampling
- Samples are drawn within pre-specified categories (i.e. strata).
Cluster Sampling
- Samples are drawn from clusters
Sampling error
Two main types of errors include selection bias and sampling error.
-
Selection Bias
Caused when the method of drawing observations skews the sample in some way. -
Sampling Error
Caused due to the random nature of drawing observations skewing the sample in some way.
Resampling
The problem of sampling is that we only have a single estimate of the population parameter, with little idea of the variability or uncertainty in the estimate.
One way to address this is by estimating the population parameter multiple times from our data sample. This is called resampling.
Serveral resampling methods include permutation, Bootstrap, Jackknife and cross validation.
The best figure telling the story of resampling:
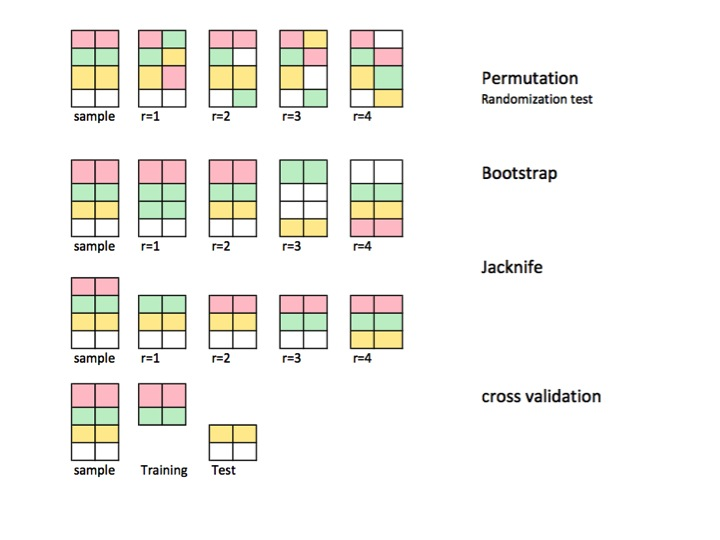
Permutation
- also called exact tests, randomisation tests, or randomisation tests
- Exchanging labels on data points when performing significance tests
Bootstrap
- Estimating precision / accuracy of sample statistics or validating models
- by drawing randomly with replacement from a set of data points.
Jackknife
- Estimating precision / accuracy of sample statistics through using subset of data
Cross validation
- Validating models by using random subsets.
Comparisons between permutations and bootstrap:
The difference between permutation and bootstrap is that bootstraps sample with replacement, and permutations sample without replacement.
The permutation test is best for testing hypotheses and bootstrapping is best for estimating confidence intervals.